
The Hidden Language of Dog Body Movements: A Canine's Silent Communication
Unlocking the Secrets Behind Your Dog’s Subtle Gestures and Movements
Jun 28, 2024 - 15:42 • 5 min read
Canines are incredibly expressive creatures, but their vocalizations are only a small part of how they communicate. Understanding the nuances of a dog’s body language can significantly enhance your bond with your furry friend and help you navigate various social interactions they might have.
Introduction
Have you ever wondered what your dog is trying to tell you with a wag of the tail or a tilt of the head? These seemingly simple gestures are part of a complex language that dogs use to convey their emotions, needs, and intentions. By learning to interpret these signals, you can foster a deeper connection with your dog, respond appropriately to their needs, and even anticipate potential issues before they escalate.

The Basics of Dog Body Language
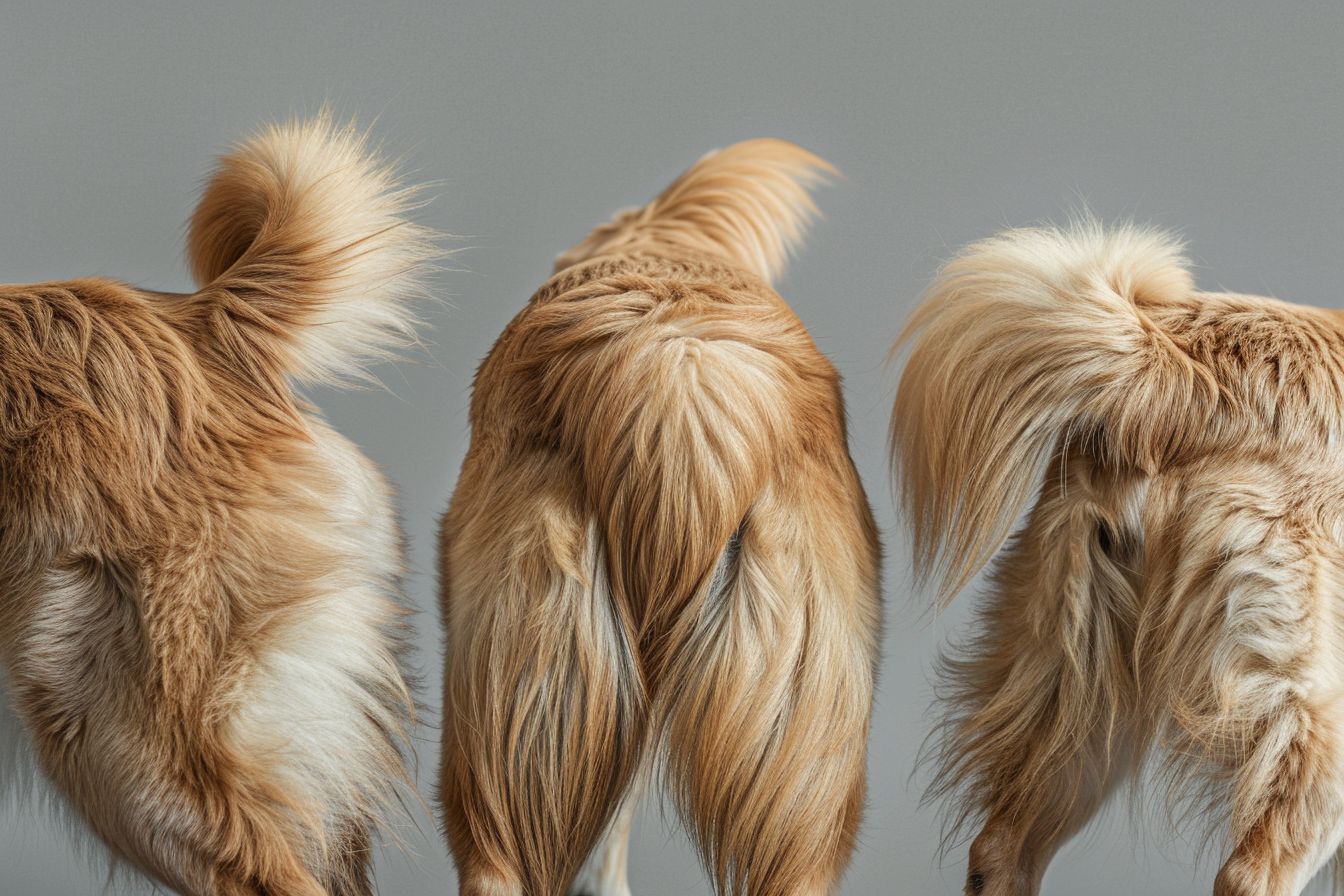
The Tail: More Than Just a Wag
Many people assume a wagging tail always signifies happiness, but this isn't always the case. The tail's position, speed, and rigidity can reveal a lot about a dog's emotional state.
1. High and Stiff: A high, rigidly wagging tail might indicate excitement or arousal, but it can also be a sign of aggression or dominance.
2. Low and Tucked: A tail that's low or tucked between the legs usually signifies fear, anxiety, or submission.
3. Neutral and Relaxed: A tail in a neutral or relaxed position may indicate that a dog is calm and comfortable.
4. Rapid Wagging: Tail wagging in a wide, rapid manner often indicates excitement and happiness, especially if accompanied by other relaxed body signals.

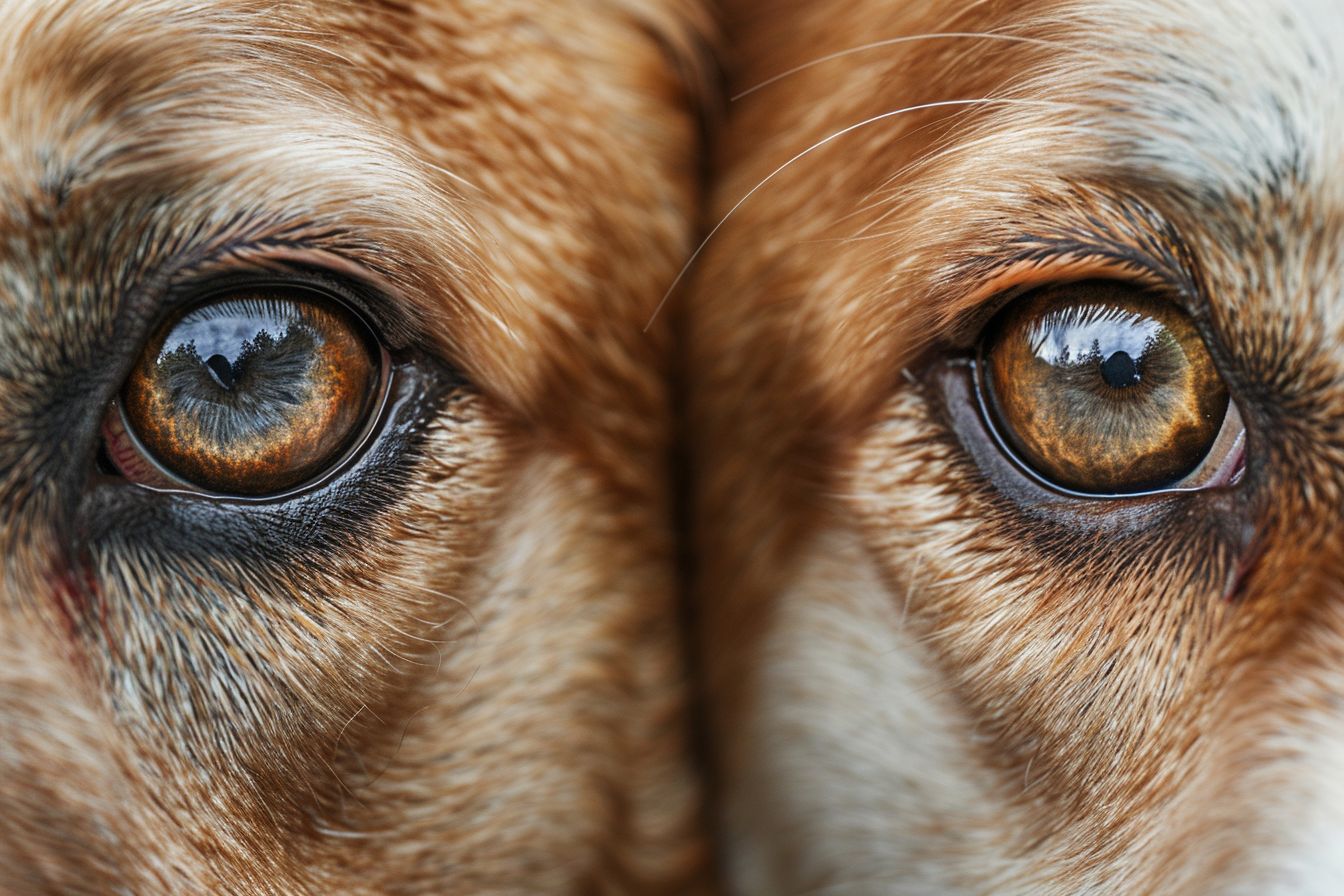
The Eyes: Windows to the Soul
A dog's eyes can speak volumes. Paying attention to the direction and intensity of a dog's gaze can provide significant insights.
1. Direct Stare: A prolonged, direct stare can be a sign of dominance or a challenge.
2. Soft Gaze: Soft, blinking eyes often indicate that a dog is relaxed and comfortable.
3. Whale Eye: When a dog shows the whites of their eyes, it generally means they're feeling anxious or threatened.
4. Avoiding Eye Contact: Avoiding direct eye contact can be a sign of submission or discomfort.

Insights and Practical Tips
The Ears: Antennas of Emotion
A dog's ears are incredibly expressive and can move in various ways to communicate different emotions.
1. Forward and Alert: Indicates interest or curiosity.
2. Flat Against the Head: This can signal fear or submission.
3. Relaxed and Neutral: Indicates a calm and relaxed dog.
4. Perked Up: Often signifies a dog is attentive and focused.

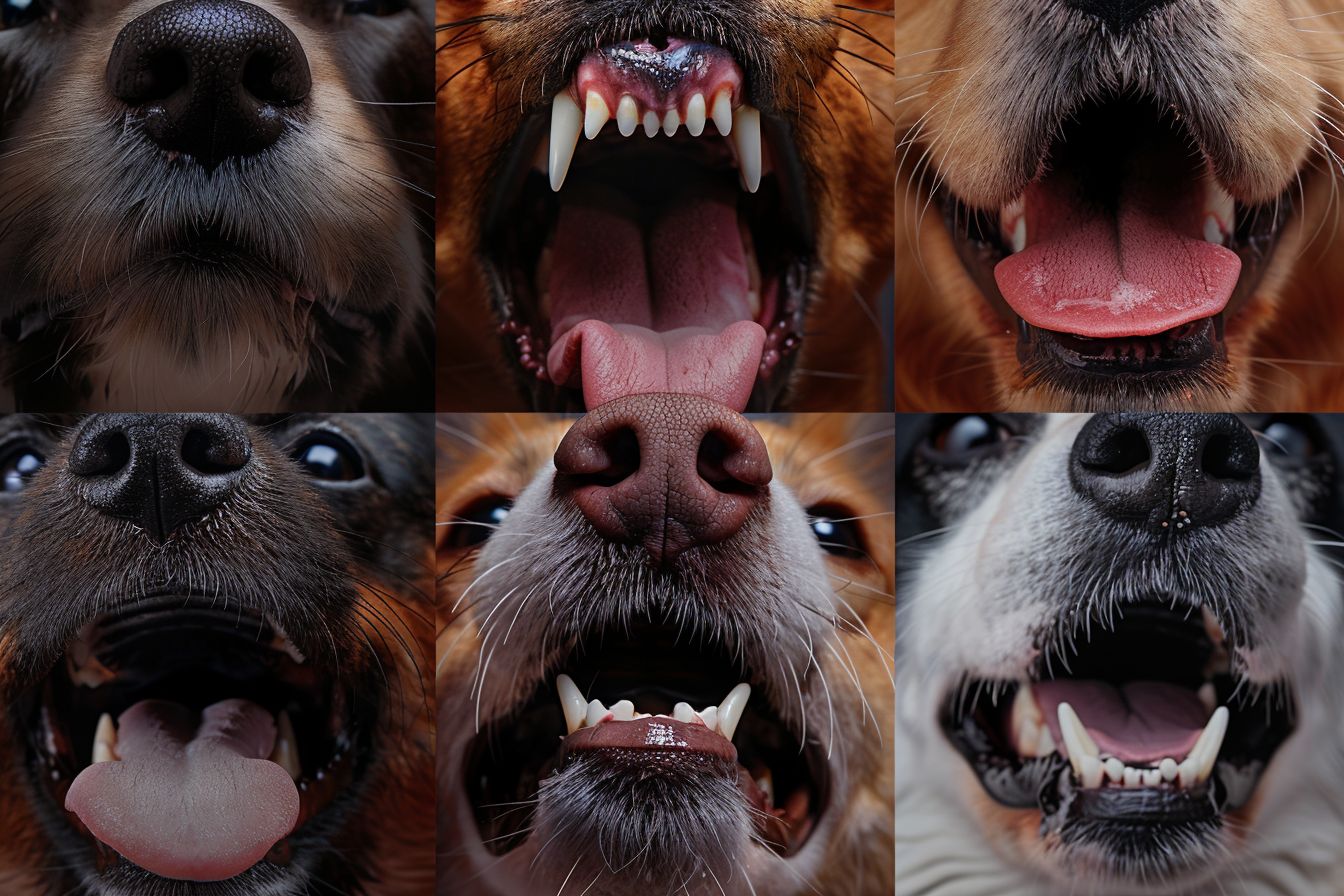
The Mouth: More Than Just Barking
Dogs use their mouths to communicate a range of emotions beyond barking and growling.
1. Yawning: While it can be a sign of tiredness, yawning also indicates stress or uncertainty in dogs.
2. Licking: Licking their lips or another dog can be a sign of submission or affection.
3. Showing Teeth: While bearing teeth can be a warning, a 'submissive grin' shows the teeth in a friendly, non-threatening way.
4. Relaxed Mouth: A slightly open, relaxed mouth often indicates contentment.

The Body: Overall Posture
A dog's overall body posture can give you a comprehensive understanding of their mood and intentions.
1. Stiff and Tall: A dog standing tall and stiff is often trying to assert dominance or is feeling threatened.
2. Crouching Low: Indicates submissive behavior or fear.
3. Relaxed and Loose: A loose, relaxed body is a sign of a happy, comfortable dog.
4. Leaning Forward: Often indicates curiosity or eagerness, but can also be a sign of impending aggression.
5. Leaning Back: Can indicate hesitation, fear, or uncertainty.
Challenges and Solutions
Misinterpretation of Signals
One common challenge is misinterpreting a dog's body language, which can lead to inappropriate responses.
Solution: Educate yourself on the basics of dog body language. There are many resources available online, and observing your dog in different situations can also be immensely helpful.
Mixed Signals
Dogs can sometimes give mixed signals, especially if they are experiencing conflicting emotions.
Solution: Look at the overall context and consider the dog's environment, recent interactions, and body language as a whole, rather than focusing on one isolated signal.
Anxiety-Related Behaviors
Some dogs display body language that indicates chronic anxiety or stress, such as excessive licking or tail tucking.
Solution: Address the underlying causes of anxiety, which may include environmental factors, past trauma, or insufficient exercise. Consulting a professional dog trainer or behaviorist can also be beneficial.

Future Trends/Outlook
Advances in Canine Behavioral Research
As technology and research methods advance, our understanding of canine behavior continues to improve. Future developments may include more sophisticated tools for analyzing and interpreting dog body language, potentially leading to better training methods and stronger human-canine bonds.
Enhanced Training Programs
With an increased emphasis on positive reinforcement and humane training methods, the future of dog training looks promising. These methods can be tailored to individual dogs based on their specific body language cues, leading to more effective and compassionate training.
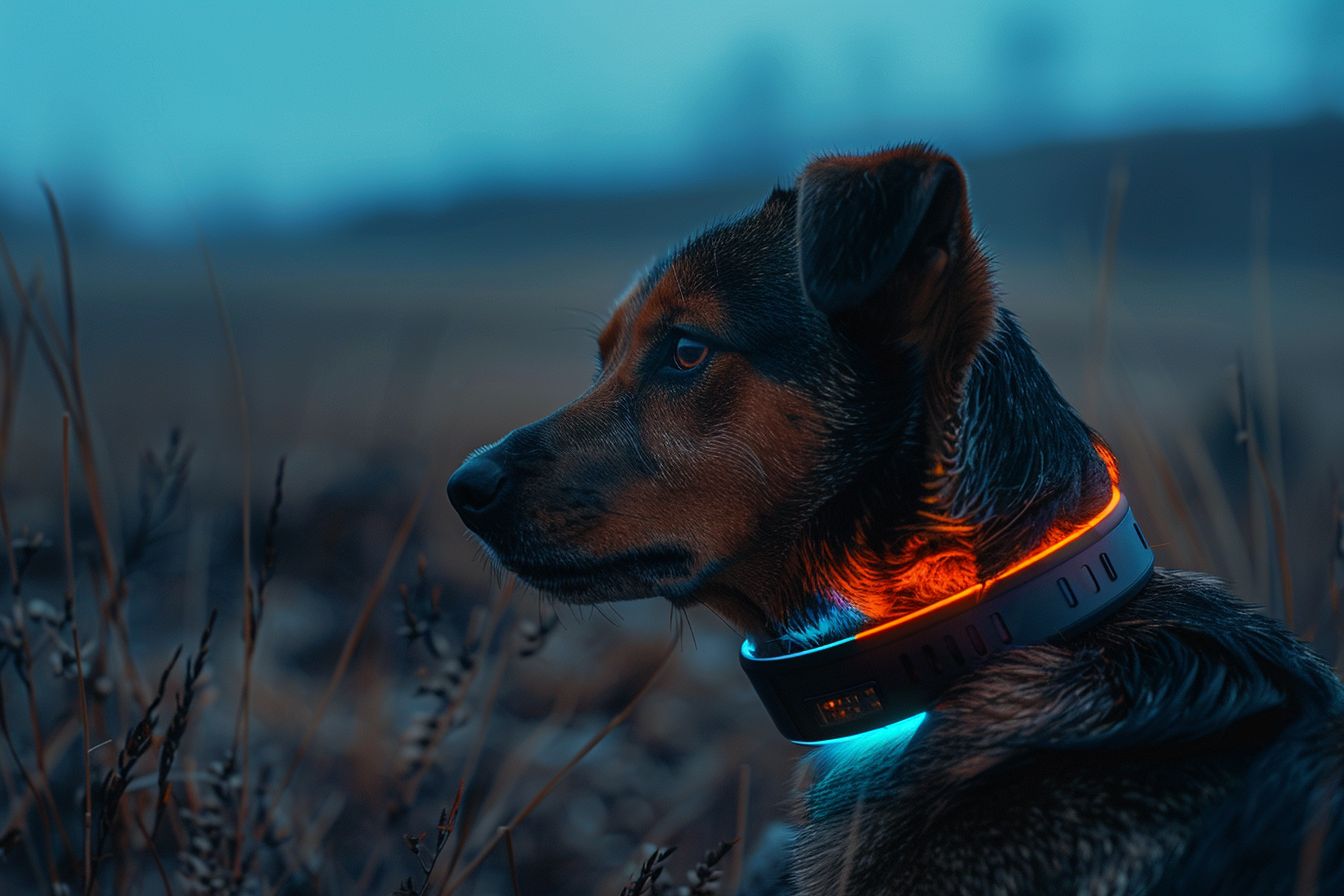
Wearable Technology
Wearable devices for dogs are becoming more sophisticated, allowing us to monitor their physiological responses in real-time. These insights can help pet owners better understand their dog's emotional state and address any issues promptly.

Conclusion
Understanding your dog's body language is a crucial aspect of responsible pet ownership. By paying attention to the subtle cues your dog provides, you can ensure they are happy, healthy, and well-adjusted. Whether you are a seasoned dog owner or a new pet parent, mastering the art of reading canine body language will undoubtedly enhance your relationship with your furry friend.
Seek professional advice before making any decisions based on the content.
